VueX
VueX是一个专为Vue.js应用程序开发的状态管理模式,采用集中式存储管理应用的所有组件的状态,并以相应的规则保证状态以一种可预测的方式发生变化,Vuex也集成到Vue的官方调试工具
基本概念
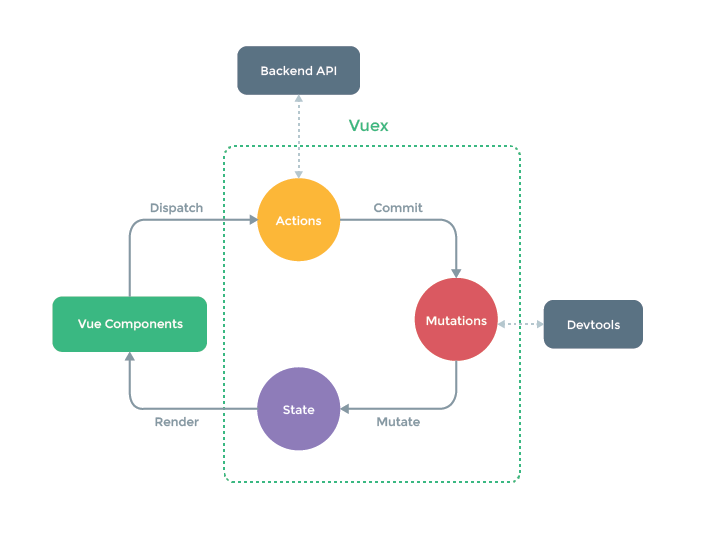
VueX具有单向数据流的概念,所有状态都存储在VueX中的State中,若组件中想使用State中的数据,直接从中获取即可,但是想若想修改State中的数据,不能直接通过State进行更改,而是通过以下流程:
- 若是异步更改State,则需要在组件中使用
dispatch()方法调用VueX中Actions中的方法,Actions中异步的调用VueX中Mutations中的方法来修改State中的数据 - 若是同步更改State,则可跳过Actions阶段,直接在组件中使用
commite()方法调用VueX中的Mutations中的方法来修改State中的数据
千万不要绕过Mutations,否则Vue-Devtools调试工具将无法检测到State的变化,并且使用VueX的意义就不存在了,可通过在创建Store对象时,添加strict: true,设置为严格模式,强制不可直接更改,切勿在生产环境下使用,否则性能会受到影响
基本使用
在注册完VueX后,Vue实例中为多出一个$store数据仓库对象,使用该对象即可访问VueX中的数据
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>hello world</title>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue/dist/vue.js"></script> <!-- CDN方式引入Vue -->
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vuex@3.6.0/dist/vuex.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<h1 @click="clickHandel">计数器{{$store.state.count}}</h1>
</div>
<script>
//Vue.use(VueX); //若使用模块化机制编程,才需要这么做
const store = new Vuex.Store({ //创建VueX数据仓库
state: { count: 0 }, //定义数据
mutations: { increment (state) { state.count++ } } //同步数据操作,state就是VueX中的state对象
})
var app = new Vue({
el: "#app",
store, //在该组件中使用VueX
methods: {
clickHandel(){ this.$store.commit('increment'); } //组件中使用commit方法对State进行修改
}
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
核心概念
State
VueX使用单一状态树,$store对象包含全部的应用状态,并且VueX状态存储是响应式的,通常会将$store 中的状态获取放入到组件的计算属性中,之后只用VueX中的数据将会更加方便
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>hello world</title>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue/dist/vue.js"></script> <!-- CDN方式引入Vue -->
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vuex@3.6.0/dist/vuex.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<h1>message:{{message}}</h1>
</div>
<script>
//Vue.use(VueX); //若使用模块化机制编程,才需要这么做
const store = new Vuex.Store({ //创建VueX数据仓库
state: { message: "message" }, //定义数据
})
var app = new Vue({
el: "#app",
store, //在该组件中使用VueX
computed: {
message(){ return this.$store.state.message }
}
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
Getters
VueX定义getters对象(可以认为是store对象的计算属性),就像计算属性一样,getter的返回值会根据它的依赖被缓存起来,且只有当它的依赖值发生了改变才会被重新计算
getter在通过方法访问时,每次都会去进行调用,而不会缓存结果
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>hello world</title>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue/dist/vue.js"></script> <!-- CDN方式引入Vue -->
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vuex@3.6.0/dist/vuex.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<h1>message:{{message}}</h1>
<h1>messageFun:{{messageFun}}</h1>
</div>
<script>
//Vue.use(VueX); //若使用模块化机制编程,才需要这么做
const store = new Vuex.Store({ //创建VueX数据仓库
state: { message: "message" }, //定义数据
getters: {
message(state, getters){
//state就是VueX中的state对象
//getters就是VueX中的getters对象,用于拿到其他的getters中的其他计算属性
console.log(getters);
return state.message + "修改"
},
messageFun(state){ //也可以通过返回一个函数,来实现给getter传参
return (arg) => { //arg就是getter传的参数
return state.message + arg
}
}
} //定义getters数据
})
var app = new Vue({
el: "#app",
store, //在该组件中使用VueX
computed: {
message(){ return this.$store.getters.message },
messageFun(){ return this.$store.getters.messageFun("arg") }
}
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
Mutations
想要修改store中的状态的唯一方法是提交mutation,Vuex中的mutation类似于事件:每个mutation都有一个字符串的事件类型和 一个回调函数,通常会将mutation 中事件触发放入到组件的方法中,用于交互更改状态
一条重要的原则:mutations中必须是同步函数
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>hello world</title>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue/dist/vue.js"></script> <!-- CDN方式引入Vue -->
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vuex@3.6.0/dist/vuex.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<h1 @click="clickHandel">计数器{{$store.state.count}}</h1>
</div>
<script>
//Vue.use(VueX); //若使用模块化机制编程,才需要这么做
const store = new Vuex.Store({ //创建VueX数据仓库
state: { count: 0 }, //定义数据
mutations: {
increment (state, payload) {
//mutations中的方法只能接收一个传递的参数,若需要传递多个参数需要使用对象方式,可在该方法内解构
state.count += payload.number;
}
}
})
var app = new Vue({
el: "#app",
store, //在该组件中使用VueX
methods: {
clickHandel(){
this.$store.commit("increment", { //commit方法中的第二个参数用于传递参数
number: 2
});
}
}
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
Actions
Actions类似于Mutations,不同在于Actions调度的是mutation,而不是直接变更状态,Action可以包含任意异步操作
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>hello world</title>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue/dist/vue.js"></script> <!-- CDN方式引入Vue -->
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vuex@3.6.0/dist/vuex.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<h1 @click="clickHandel">计数器{{$store.state.count}}</h1>
</div>
<script>
//Vue.use(VueX); //若使用模块化机制编程,才需要这么做
const store = new Vuex.Store({ //创建VueX数据仓库
state: { count: 0 }, //定义数据
mutations: {
increment (state, payload) { state.count += payload.number }
},
actions: {
incrementAsync (state, payload) {
//与mutations一样,actions中的方法只能接收一个传递的参数,若需要传递多个参数需要使用对象方式,可在该方法内解构
setTimeout(()=>{ state.commit("increment", payload) },500);
}
}
})
var app = new Vue({
el: "#app",
store, //在该组件中使用VueX
methods: {
clickHandel(){
this.$store.dispatch("incrementAsync", { //dispatch方法中的第二个参数用于传递参数
number: 2
});
}
}
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
Modules
当全局只使用一个Store时,应用的所有状态会集中到一个比较大的对象,当应用变得非常复杂时,store对象就有可能变得相当臃肿,为了解决这个问题,可以将Store割成模块,每个模块拥有自己的states、mutations、actions、getters、甚至是嵌套子模块
默认情况下,除states外,模块内部的actions、mutations和getters是注册在全局命名空间的,可为模块单独添加namespaced: true来开启模块内部命名空间,调用方式需要添加命名空间进行调用,该命名空间使用的是反斜杠作为分隔符
模块可以在创建Store时一同创建,也可以使用Store实例的方法进行动态创建registerModule(moduleName,options)
,也可以使用unregisterModule(moduleName)动态删除模块(moduleName若是数组则是嵌套模块)
State
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>hello world</title>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue/dist/vue.js"></script> <!-- CDN方式引入Vue -->
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vuex@3.6.0/dist/vuex.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<h1>{{oneMessage}}</h1>
<h1>{{twoMessage}}</h1>
</div>
<script>
//Vue.use(VueX); //若使用模块化机制编程,才需要这么做
const moduleOne = {
state: { message: "oneMessage" },
}
const moduleTwo = {
state: { message: "twoMessage" },
}
//定义两个模块,用于在创建Store时注册
const store = new Vuex.Store({ //创建VueX数据仓库
modules: {
one: moduleOne,
two: moduleTwo
}
})
var app = new Vue({
el: "#app",
store, //在该组件中使用VueX
computed: {
oneMessage(){ return this.$store.state.one.message }, //使用时先通过该命名空间在访问到模块中的state
twoMessage(){ return this.$store.state.two.message } //使用时先通过该命名空间在访问到模块中的state
}
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
Getter
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>hello world</title>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue/dist/vue.js"></script> <!-- CDN方式引入Vue -->
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vuex@3.6.0/dist/vuex.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<h1>{{oneMessage}}</h1>
<h1>{{twoMessage}}</h1>
</div>
<script>
//Vue.use(VueX); //若使用模块化机制编程,才需要这么做
const moduleOne = {
state: { message: "oneMessage" },
getters: {
message(state, getters, rootState){
//state和getters是局部的state和的getters对象
//rootState是根的state对象
console.log(rootState);
return state.message + "修改"
}
}
}
const moduleTwo = {
namespaced: true,
state: { message: "twoMessage" },
getters: { message(state){ return state.message + "修改" } }
}
//定义两个模块,用于在创建Store时注册
const store = new Vuex.Store({ //创建VueX数据仓库
modules: {
one: moduleOne,
two: moduleTwo
}
})
var app = new Vue({
el: "#app",
store, //在该组件中使用VueX
computed: {
oneMessage(){ return this.$store.getters.message }, //未开启模块命名空间会全局注册,直接使用即可
twoMessage(){ return this.$store.getters["two/message"] } //开启模块命名空间,需使用ES5方括号方式进行调用
}
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
Mutations
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>hello world</title>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue/dist/vue.js"></script> <!-- CDN方式引入Vue -->
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vuex@3.6.0/dist/vuex.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<h1 @click="oneClick">{{oneMessage}}</h1>
<h1 @click="twoClick">{{twoMessage}}</h1>
</div>
<script>
//Vue.use(VueX); //若使用模块化机制编程,才需要这么做
const moduleOne = {
state: { message: "oneMessage" },
mutations: {
addMessage(state, payload){ //state是局部的state对象
state.message += payload.message;
}
}
}
const moduleTwo = {
namespaced: true,
state: { message: "twoMessage" },
mutations: {
addMessage(state, payload){ //state是局部的state对象
state.message += payload.message;
}
}
}
//定义两个模块,用于在创建Store时注册
const store = new Vuex.Store({ //创建VueX数据仓库
modules: {
one: moduleOne,
two: moduleTwo
}
})
var app = new Vue({
el: "#app",
store, //在该组件中使用VueX
computed: {
oneMessage(){ return this.$store.state.one.message },
twoMessage(){ return this.$store.state.two.message }
},
methods: {
oneClick(){ this.$store.commit("addMessage",{ message: " add one" }) }, //未开启模块命名空间会全局注册,直接使用即可
twoClick(){ this.$store.commit("two/addMessage", { message: " add two" }) } //开启模块命名空间,需添加命名空间进行触发
}
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
Actions
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>hello world</title>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue/dist/vue.js"></script> <!-- CDN方式引入Vue -->
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vuex@3.6.0/dist/vuex.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<h1 @click="oneClick">{{oneMessage}}</h1>
<h1 @click="twoClick">{{twoMessage}}</h1>
</div>
<script>
//Vue.use(VueX); //若使用模块化机制编程,才需要这么做
const moduleOne = {
state: { message: "oneMessage" },
mutations: {
addMessage(state, payload){ //state是局部的state对象
state.message += payload.message;
}
},
actions: {
addMessageAsync(ctx, payload){
setTimeout(() => { ctx.commit("addMessage", payload) }, 500);
}
}
}
const moduleTwo = {
namespaced: true,
state: { message: "twoMessage" },
mutations: {
addMessage(state, payload){ //state是局部的state对象
state.message += payload.message;
}
},
actions: {
addMessageAsync(ctx, payload){
//ctx中的commit、dispatch方法已局部化
//想要调用全局的方法则需要将将{ root: true }作为第三参数传给dispatch或commit即可
setTimeout(() => { ctx.commit("addMessage", payload) }, 500);
}
}
}
//定义两个模块,用于在创建Store时注册
const store = new Vuex.Store({ //创建VueX数据仓库
modules: {
one: moduleOne,
two: moduleTwo
}
})
var app = new Vue({
el: "#app",
store, //在该组件中使用VueX
computed: {
oneMessage(){ return this.$store.state.one.message },
twoMessage(){ return this.$store.state.two.message }
},
methods: {
oneClick(){ this.$store.dispatch("addMessageAsync", { message: " add one" }) }, //未开启模块命名空间会全局注册,直接使用即可
twoClick(){ this.$store.dispatch("two/addMessageAsync", { message: " add two" }) } //开启模块命名空间,需添加命名空间进行触发
}
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
Map辅助函数解构
当一个组件需要获取多个state、getters、mutations和actions时,都声明为计算属性或方法会有些重复和冗余。为了解决这个问题,VueX提供了相应的Map方法,用于解构后生成相应的计算属性和方法,之后使用this即可,Map方法中可接收数组或对象,用于提取store中对应的方法
- 数组方式:与store中同名,通常用数组方式即可
- 对象方式:可以自定义名,若是Modules则值必须是一个函数
- 值可以是一个字符串,与数组中的一样
- 值也可以是一个函数,函数的第一个参数就是state、getters、mutations或actions
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>hello world</title>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue/dist/vue.js"></script> <!-- CDN方式引入Vue -->
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vuex@3.6.0/dist/vuex.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<h1 @click="incrementAsync">计数器{{countFun}}</h1>
<h1 @click="increment">计数器{{count}}</h1>
</div>
<script>
//Vue.use(VueX); //若使用模块化机制编程,才需要这么做
const store = new Vuex.Store({ //创建VueX数据仓库
state: { count: 0 }, //定义数据
getters: { countFun(state){ return state.count + "修改" } },
mutations: { increment (state) { state.count++ } },
actions: { incrementAsync (state) { setTimeout(()=>{ state.commit("increment") },500); } }
})
var app = new Vue({
el: "#app",
store, //在该组件中使用VueX
computed: {
...Vuex.mapState(["count"]),
...Vuex.mapGetters(["countFun"]),
},
methods: {
...Vuex.mapMutations(["increment"]),
...Vuex.mapActions(["incrementAsync"]),
}
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
插件
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>hello world</title>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue/dist/vue.js"></script> <!-- CDN方式引入Vue -->
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vuex@3.6.0/dist/vuex.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<h1 @click="clickHandel">计数器{{$store.state.count}}</h1>
</div>
<script>
//Vue.use(VueX); //若使用模块化机制编程,才需要这么做
function myPlugin(store){ //store就是当前插件作用于的Vuex.Store对象
store.subscribe((mutation, state) => { //订阅mutations中事件的触发
console.log("subscribe:", mutation.type); //mutation.type是mutations中的事件
console.log("subscribe:", mutation.payload); //mutation.payload是传递给mutations中的事件的payload参数
console.log("subscribe:", store.state === state); //state就是store.tate
})
store.subscribeAction((action, state) => { //订阅actions中事件的触发
console.log("subscribeAction:", action.type); //action.type是actions中的事件
console.log("subscribeAction:", action.payload); //action.payload是传递给actions中的事件的payload参数
console.log("subscribeAction:", store.state === state); //state就是store.tate
})
store.watch((state) => { //监听state中某个状态的变化
return state.count //返回要监听的状态
}, (newCount) => { //变化后要执行的函数
console.log(newCount); //newCount是变化后的值
})
}
const store = new Vuex.Store({ //创建VueX数据仓库
state: { count: 0, }, //定义数据
mutations: { increment (state, payload) { state.count += payload.number } },
actions: { incrementAsync (state, payload) { setTimeout(()=>{ state.commit("increment", payload) }, 500) } },
plugins: [myPlugin] //注册插件
})
var app = new Vue({
el: "#app",
store, //在该组件中使用VueX
methods: {
clickHandel(){ this.$store.dispatch("incrementAsync", {number: 2}); }
}
});
</script>
</body>
</html>

Comments NOTHING